Anatomy
Knee Anatomy
The knee is a complex joint made up of different structures - bones, tendons, ligaments, and muscles. They all work together to maintain the knee’s normal function and provide stability to the knee during movement.
Having a well-functioning healthy knee is essential for our mobility and ability to participate in various activities. Understanding the anatomy of the knee enhances your ability to discuss and choose the right treatment procedure for knee problems with your doctor.
Bones of the Knee
The knee is a hinge joint made up of two bones, the thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia). There are two round knobs at the end of the femur called femoral condyles that articulate with the flat surface of the tibia called the tibial plateau. The tibial plateau on the inside of the leg is called the medial tibial plateau and on the outside of the leg, the lateral tibial plateau.
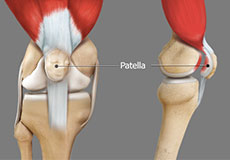
The two femoral condyles form a groove on the front (anterior) side of the knee called the patellofemoral groove. A small bone called the patella sits in this groove and forms the kneecap. It acts as a shield and protects the knee joint from direct trauma.
A fourth bone called the fibula is the other bone of the lower leg. This forms a small joint with the tibia. This joint has very little movement and is not considered a part of the main joint of the knee.
Articular Cartilage and Menisci of the Knee
Movement of the bones causes friction between the articulating surfaces. To reduce this friction, all articulating surfaces involved in the movement are covered with a white, shiny, slippery layer called articular cartilage. The articulating surface of the femoral condyles, tibial plateaus and the back of the patella are covered with this cartilage. The cartilage provides a smooth surface that facilitates easy movement.
To further reduce friction between the articulating surfaces of the bones, the knee joint is lined by a synovial membrane that produces a thick clear fluid called synovial fluid. This fluid lubricates and nourishes the cartilage and bones inside the joint capsule.
Within the knee joint, between the femur and tibia, are two C-shaped cartilaginous structures called menisci. Menisci function to provide stability to the knee by spreading the weight of the upper body across the whole surface of the tibial plateau. The menisci help in load-bearing i.e. it prevents the weight from concentrating onto a small area, which could damage the articular cartilage. The menisci also act as a cushion between the femur and tibia by absorbing the shock produced by activities such as walking, running and jumping.
Ligaments of the Knee
Ligaments are tough bands of tissue that connect one bone to another bone. The ligaments of the knee stabilize the knee joint. There are two important groups of ligaments that hold the bones of the knee joint together, collateral and cruciate ligaments.
Collateral ligaments are present on either side of the knee. They prevent the knee from moving too far during side to side motion. The collateral ligament on the inside is called the medial collateral ligament (MCL) and the collateral ligament on the outside is called the lateral collateral ligament (LCL).
Cruciate ligaments, present inside the knee joint, control the back-and-forth motion of the knee. The cruciate ligament in the front of the knee is called anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the cruciate ligament in the back of the knee is called posterior cruciate ligament (PCL).
Muscles of the Knee
There are two major muscles in the knee - the quadriceps and the hamstrings, which enable movement of the knee joint. The quadriceps muscles are located in front of the thigh. When the quadriceps muscles contract, the knee straightens. The hamstrings are located at the back of the thigh. When the hamstring muscles contract, the knee bends.
Tendons of the Knee
A tendon is a tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone. The quadriceps muscles of the knee meet just above the patella and attach to it through a tendon called the quadriceps tendon. The patella further attaches to the tibia through a tendon called the patella tendon. The quadriceps muscle, quadriceps tendon, and patellar tendon all work together to straighten the knee. Similarly, the hamstring muscles at the back of the leg are attached to the knee joint with the hamstring tendon.
Knee Conditions
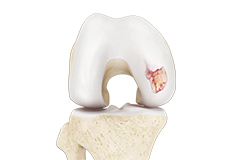
Knee Arthritis
The joint surface is covered by a smooth articular surface that allows pain-free movement in the joint. Arthritis is a general term covering numerous conditions where the joint surface or cartilage wears out.
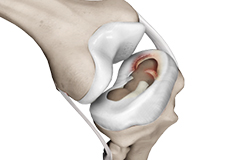
Meniscal Tears
A meniscal tear is a common knee injury in athletes, especially those involved in contact sports. A sudden bend or twist in your knee causes the meniscus to tear.
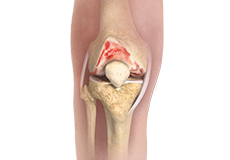
Knee Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis also called degenerative joint disease, is the most common form of arthritis. It occurs most often in older people. This disease affects the tissue covering the ends of bones in a joint (cartilage).
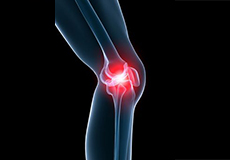
Knee Pain
Knee pain is a common condition affecting individuals of various age groups. It not only affects movement but also impacts your quality of life.

Knee Injury
Pain, swelling, and stiffness are the common symptoms of any damage or injury to the knee. If care is not taken during the initial phases of injury, it may lead to joint damage, which may end up destroying your knee.
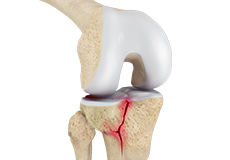
Knee Fracture
A fracture is a condition in which there is a break in the continuity of the bone. In younger individuals, these fractures are caused by high energy injuries, as from a motor vehicle accident.
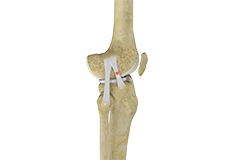
Knee Sprain
Knee sprain is a common injury that occurs from overstretching of the ligaments that support the knee joint. A knee sprain occurs when the knee ligaments are twisted or turned beyond its normal range, causing the ligaments to tear.
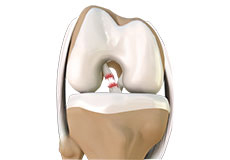
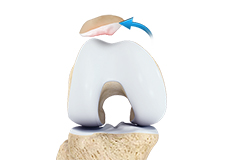
Patellar Instability
Any damage to the supporting ligaments may cause the patella to slip out of the groove either partially (subluxation) or completely (dislocation).
Anterior Knee Pain
Anterior knee pain is characterized by chronic pain over the front and center of the knee joint. It is common in athletes, active adolescents (especially girls) and overweight individuals.
Chondromalacia Patella
Chondromalacia patella is a common condition characterized by softening, weakening and damage of the cartilage. The condition is most often seen in young athletes and older adults who have arthritis of the knee.
Fractures of the Patella
The patella or kneecap is a small bone present in the front of your knee where the thigh bone meets the shinbone. It provides protection to your knee and attachment to muscles in the front of the thigh.
Fractures of the Tibia
The lower leg is made up of two long bones called the tibia and fibula that extend between the knee and ankle. The tibia or shinbone is the larger of the two bones.
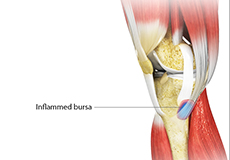
Goosefoot Bursitis of the Knee
A bursa is a small fluid-filled sac found between soft tissues and bones. It lubricates and acts as a cushion, decreasing the friction between bones when they move. Bursitis refers to the inflammation and swelling of the bursa.
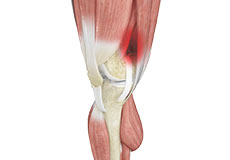
Iliotibial Band Syndrome
An iliotibial band is a tough group of fibers that runs from the iliac crest of the hip along the outside of the thigh, till the outer side of the shinbone, just below the knee joint.
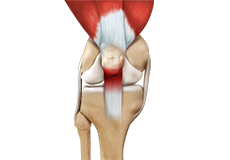
Jumper's Knee
Jumper’s knee, also known as patellar tendinitis, is inflammation of the patellar tendon that connects your kneecap (patella) to your shinbone. This tendon helps in the extension of the lower leg.
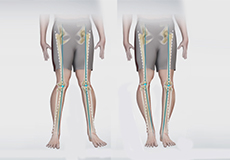
Knee Angular Deformities
Angular deformities of the knee are variations in the normal growth pattern during early childhood and are common during childhood.
Knee Infection
Knee infection is a serious medical condition that needs immediate treatment. Infection may occur followed by a knee replacement surgery or trauma and is usually caused by bacteria. Infection may spread to the space of the knee joint or deep layers of your knee causing serious complications.
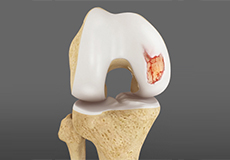
Articular Cartilage Injury
Articular or hyaline cartilage is the tissue lining the surface of the two bones in the knee joint. Cartilage helps the bones move smoothly against each other and can withstand the weight of the body during activities such as running and jumping.
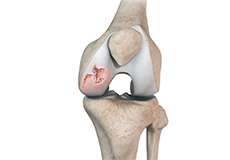
Chondral or Articular Cartilage Defects
The articular or hyaline cartilage is the tissue lining the surface of the two bones in the knee joint. Cartilage helps the bones move smoothly against each other and can withstand the weight of your body during activities such as running and jumping.

Knee Sports Injuries
Trauma is any injury caused during physical activity, motor vehicle accidents, electric shock, or other activities. Sports trauma or sports injuries refer to injuries caused while playing indoor or outdoor sports and exercising.
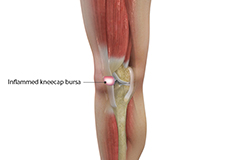
Kneecap Bursitis
Bursitis refers to the inflammation and swelling of the bursa. Inflammation of the bursa in front of the kneecap (patella) is known as kneecap bursitis or prepatellar bursitis.
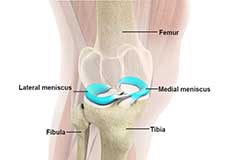
Lateral Meniscus Syndrome
Lateral meniscus syndrome is characterized by an injury caused by the tearing of the cartilage tissue or a rare case of a congenital abnormality called a discoid meniscus, which results in knee pain.
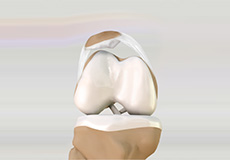
Lateral Patellar Compression Syndrome
Lateral patellar compression syndrome refers to pain under and around your kneecap. It is a common complaint among runners, jumpers and other athletes such as skiers, cyclists, and soccer players.
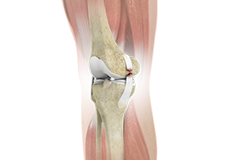
Ligament Injuries
The knee is a hinge joint made up of two bones, the thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia). Ligaments are tough bands of tissue that connect one bone to another bone. The ligaments of the knee stabilize the knee joint.
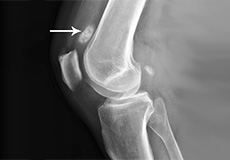
Loose Bodies in the Knee
Loose bodies are fragments of detached cartilage or bone inside the knee joint. These fragments may be free floating (unstable) or may be trapped (stable) within the joint. Depending on the severity, you may have one or more loose bodies in your knee joint.
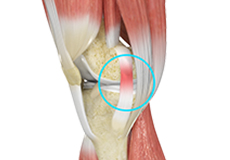
MCL Sprains
The medial collateral ligament (MCL), a band of tissue present on the inside of your knee joint, connects your thighbone and shinbone (bone of your lower leg). The MCL maintains the integrity of the knee joint and prevents it from bending inward.

Meniscal Injuries
Meniscal tears are one of the most common injuries to the knee joint. It can occur at any age but are more common in athletes involved in contact sports. The meniscus has no direct blood supply and for that reason, when there is an injury to the meniscus, healing is difficult.

Medial Meniscus Syndrome
Medial meniscal injuries are usually considered as either traumatic or degenerative. Whilst degenerate tears may present with a gradual history of increasing symptoms, traumatic injuries will usually occur as the knee is extended and rotated from a flexed position against resistance.
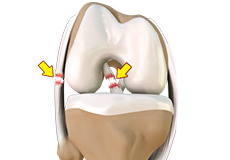
Multiligament Instability
The knee is a complex joint of the body that is vital for movement. The four major ligaments of the knee are anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL) and lateral collateral ligament (LCL).

Posterolateral Instability
Posterolateral instability, also known as posterolateral rotatory instability (PLRI), is a common pattern of knee instability that results from injuries to the structures that support the outside of the knee joint, the posterolateral corner.
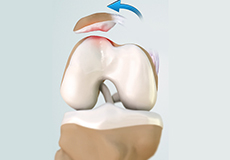
Patellofemoral Instability
Any damage to the supporting ligaments may cause the patella to slip out of the groove either partially (subluxation) or completely (dislocation). This misalignment can damage the underlying soft structures such as muscles and ligaments that hold the kneecap in place.
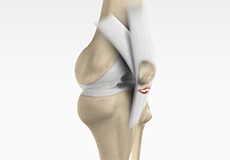
Patellar Tendon Rupture
The patellar tendon works together with the quadriceps muscle and the quadriceps tendon to allow your knee to straighten out. Patella tendon rupture is the rupture of the tendon that connects the patella (kneecap) to the top portion of the tibia (shinbone).
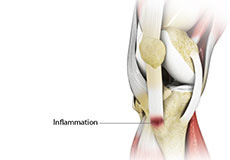
Osgood Schlatter Disease
Osgood-Schlatter disease refers to a condition in older children and teenagers caused by excessive stress to the patellar tendon (located below the kneecap). Participants in sports such as soccer, gymnastics, basketball, and distance running are at higher risk for this disease.

Multiligament Knee Injuries
Injury to more than one knee ligament is called a multiligament knee injury and may occur during sports or other physical activities.

Osteochondral Defect of the Knee
An osteochondral defect, also commonly known as osteochondritis dissecans, of the knee refers to a damage or injury to the smooth articular cartilage surrounding the knee joint and the bone underneath the cartilage.
Osteonecrosis of the Knee
Osteonecrosis is a condition in which the death of a section of bone occurs because of lack of blood supply to it. It is one of the most common causes of knee pain in older women. Women over 60 years of age are commonly affected, three times more often than men.
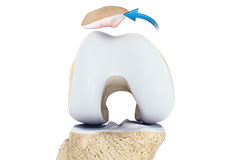
Patellar Dislocation/Patellofemoral Dislocation
Patellar dislocation occurs when the patella moves out of the patellofemoral groove, (trochlea) onto the bony head of the femur. If the kneecap partially comes out of the groove, it is called subluxation; if the kneecap completely comes out, it is called dislocation (luxation).
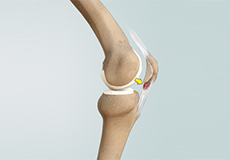
Patellar Tendinitis
Patellar tendinitis, also known as "jumper's knee", is an inflammation of the patellar tendon that connects your kneecap (patella) to your shinbone. This tendon helps in extension of the lower leg.

Patellar Tracking Disorder/Patellar Maltracking
Patellar tracking disorder, also known as patellar maltracking, is a condition in which the kneecap (patella) moves sideways from its groove when the leg is bent or straightened.
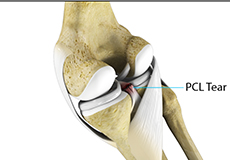
PCL Injuries
Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), one of the four major ligaments of the knee, is situated at the back of the knee. It connects the thighbone (femur) to the shinbone (tibia). The PCL limits the backward motion of the shinbone.
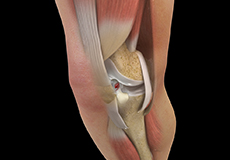
Pediatric ACL Tears
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is a ligament that provides stability, reduces stress and prevents the knee from rotating or slipping out of position while jumping, running and landing. This ligament can tear during sports activities and exercise, as a result of a non-contact twisting injury, and is becoming a common injury in children.

Periprosthetic Knee Infection
A very small percentage of patients (less than 1%) who undergo knee replacement may develop an infection around the knee joint. This infection is called a periprosthetic knee infection.

Pes Anserine Bursitis
Bursitis refers to the inflammation and swelling of a bursa. A bursa is a small fluid-filled sac found between soft tissues and bones that lubricates and acts as a cushion to decrease friction between bones when they move.
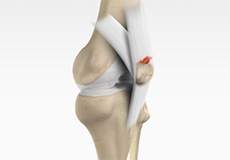
Quadriceps Tendon Rupture
The quadriceps tendon is a thick tissue located at the top of the kneecap. It works together with the quadriceps muscles to allow us to straighten our leg. The quadriceps muscles are the muscles located in front of the thigh.
Runner's Knee
Patellofemoral pain syndrome also called runner’s knee refers to pain under and around your kneecap. Patellofemoral pain is associated with a number of medical conditions such as anterior knee pain syndrome, patellofemoral malalignment, and chondromalacia patella.
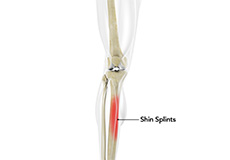
Shin Splints
Shin splints are pain and inflammation of the tendons, muscles and bone tissue along the tibia or shinbone (lower leg). It occurs because of vigorous physical activities such as exercise or sports. The condition is also referred to as medial tibial stress syndrome (MTSS).

Patella Fracture
The kneecap or patella forms a part of the knee joint. It is present at the front of the knee, protecting the knee and providing attachment to various muscle groups of the thigh and leg.

Periprosthetic Knee Fractures
Knee replacement, also called knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which the worn-out or damaged surfaces of the knee joint are removed and replaced with artificial implants. Any resulting fractures or breaks in the bone around the implant are called periprosthetic knee fractures.

Tibial Eminence Fractures
A tibial eminence fracture is break or crack in the bony attachment of the ACL to the tibia. The fracture can be a contact or non-contact injury and occurs at the base of the tibial eminence.
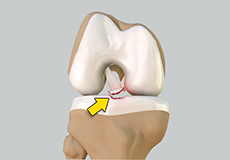
Tibial Eminence Spine Avulsion Fracture
Tibial eminence spine avulsion fracture is the avulsion (tearing away) of the tibial eminence. This injury may occur because of abnormal outward bending or twisting injuries caused by a sudden halt of moving joints, excessive flexion (bending inwards) and internal rotation, which usually occur during skiing and motor vehicle accidents.

Tibial Plateau Fracture
A tibial plateau fracture is a crack or break on the top surface of the tibia or shinbone in the knee joint. The fracture most often occurs following a high-intensity trauma or injury from the impaction of the femoral condyles over the tibial plateau.
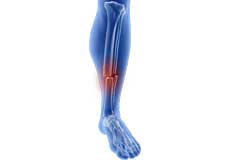
Tibial Shaft Fracture
A tibial shaft fracture is a crack or break in the middle section of the tibia bone due to severe trauma. The lower leg is made up of two long bones called the tibia and fibula that extend between the knee and ankle and help form the ankle joint and knee joint.

Tibial Eminence Fracture
The tibia or shin bone is a major bone of the leg which connects the knee to the ankle. A fracture or break in the upper part of the tibia is known as a proximal tibial fracture and commonly occurs just below the knee joint.
Knee Procedures
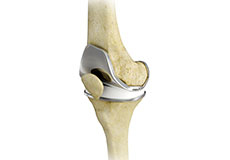
Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement, also called total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which the worn out or damaged surfaces of the knee joint are removed and replaced with an artificial prosthesis.

Outpatient Total Knee Replacement
Outpatient total knee replacement is considered when your vital signs are stable, such as heart and respiratory rate, blood pressure, and temperature. Moreover, you need to be able to maintain pain control with oral medication and tolerate a regular diet before being discharged on the same day of surgery.
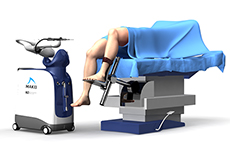
Robotic Assisted Knee Replacement
Robotic-assisted knee replacement surgery is an alternative to the conventional knee replacement procedure. It is performed using robotic-arm technology that allows your surgeon to precisely perform the surgery through a smaller incision as compared to traditional surgery.
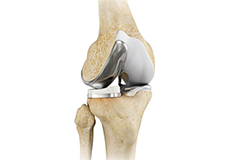
Unicompartmental/Partial Knee Replacement
Unicompartmental knee replacement is a minimally invasive surgery in which only the damaged compartment of the knee is replaced with an implant. It is also called a partial knee replacement.
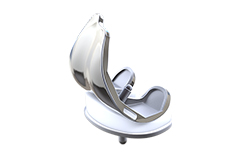
Custom Knee Replacement
Custom Knee Replacement is an advanced surgical procedure in which the damaged knee joint is replaced by a customized implant, specifically designed to match the unique size and shape of each patient’s knee.
Knee Arthroscopy
Knee arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure performed using an arthroscope, a viewing instrument, to diagnose or treat a knee problem. It is a relatively safe procedure and you will usually be discharged from the hospital on the same day of surgery.
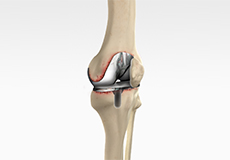
Revision Knee Replacement
Revision knee replacement surgery involves replacing a part or all your previous knee prosthesis with a new prosthesis. Although total knee replacement surgery is successful, sometimes the procedure can fail due to various reasons and may require a second revision surgery.

Robotic Unicondylar Knee Replacement
A unicondylar knee replacement is a procedure to replace part of the knee joint with a prosthetic implant to relieve pain and improve the function of the joint. Advances in technology have allowed this procedure to be performed in a minimally invasive manner with robotic assistance.
Unicondylar knee Replacement
Unicompartmental knee replacement or unicondylar knee replacement is a minimally invasive surgery in which only the damaged compartment of the knee is replaced with an implant. It is also called a partial knee replacement.
Minimally Invasive Knee Joint Replacement
Total knee replacement is a very successful surgical treatment for knee arthritis. Over the years, minimally invasive knee replacement surgical techniques have been developed to lessen tissue trauma and improve patient outcomes.
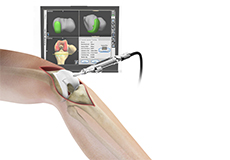
Computer Navigation for Total Knee Replacement
Computer navigation provides your surgeon with real-time 3-D images of your mapped knee and the surgical instruments during surgery. The data for the images is provided by infrared sensors fixed to the bones of the knee and surgical instruments.
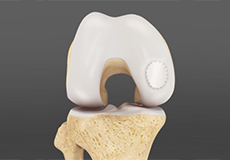
Cartilage Replacement
Cartilage replacement is a surgical procedure performed to replace the worn-out cartilage with new cartilage. It is usually performed to treat small areas of cartilage damage usually caused by sports or traumatic injuries. It is not indicated if you have advanced arthritis of the knee.
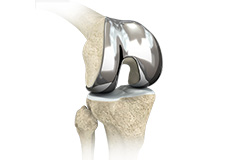
Custom-fitted Total Knee Arthroplasty
Custom-fitted total knee arthroplasty is a newer more advanced technology in total knee replacement surgery that uses an individualized patient-specific knee implant for the replacement of all three components of the knee.
Outpatient Unicondylar Knee Replacement
A unicondylar knee replacement, also known as unicompartmental or partial knee replacement, is a procedure to replace a portion of the damaged knee joint with a prosthetic implant to relieve pain and improve function of the knee joint.

Knee Replacement with OrthAlign Technology
OrthAlign® uses a technology that simplifies and enhances the precision in implant alignment, significantly improving procedure outcomes. The knee joint consists of three bones: the femur (thighbone), the tibia (shinbone) and the patella (kneecap).

Lateral Approach Total Knee Replacement
Lateral approach total knee replacement is a surgical procedure employed for the treatment of valgus deformity of the osteoarthritic knee. The procedure involves approaching the knee joint from the lateral side of the patella (kneecap) or on the outer aspect of the knee to remove and replace the worn-out or damaged surfaces of the knee joint with a prosthesis to treat valgus deformity of the knee.
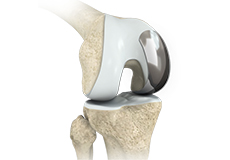
Partial Lateral Knee Replacement
Partial lateral knee replacement is a surgery to replace only the lateral part of your damaged knee. It is also called unicompartmental knee replacement.

Partial Medial Knee Replacement
Partial medial knee replacement is a surgery to replace only the medial part of your damaged knee. It is also called unicompartmental knee replacement.

Tricompartmental Knee Replacement
Tricompartmental knee replacement, also called total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which the worn-out or damaged surfaces of the knee joint are removed and replaced with artificial parts.

Visionaire Knee Replacement
Visionaire is an advanced surgical technology for a joint replacement that is based on the patient’s specific anatomy. Surgical instruments are designed according to X-ray, MRI or CT scan images of your knee joint.

Patient Specific Knee Replacement
Patient Specific Knee Replacement is a newer technology in total knee replacement surgery. It is an advanced procedure using an individualized patient-specific knee implant for replacement of all three components of the knee.
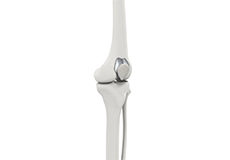
Patellofemoral Knee Replacement
Traditionally, arthritis in only one compartment of the knee is treated by partial knee replacement surgery. Patellofemoral knee replacement is a minimally invasive surgical option performed in the patellofemoral compartment only, preserving the knee parts not damaged by arthritis as well as the stabilizing anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments (ACL and PCL).
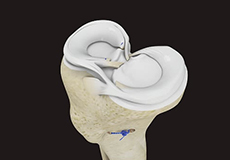
Meniscus Replacement
Meniscus replacement is a surgical procedure performed to replace a torn or damaged meniscus in the knee. The meniscus is a soft, fibrous disk of cartilage in your knee joint that sits between the femur (thighbone) and the tibia (shinbone).

Patellar Tendon Repair
Patellar tendon repair is the surgery performed to reattach the torn tendon to the kneecap and to restore normal function in the affected leg.

Quadriceps Tendon Repair
Quadriceps tendon is a thick tissue located at the top of the kneecap. The quadriceps tendon works together with the quadriceps muscles to allow us to straighten our leg. The quadriceps muscles are the muscles located in front of the thigh.
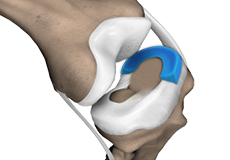
Meniscal Surgery
Meniscal surgery is a surgical procedure employed for the treatment of torn or damaged meniscal tissues in the knee. It is mostly performed as a minimally invasive keyhole procedure.

Knee Fracture Surgery
A knee fracture is a broken bone or a crack in or around the joint of the knee. This can involve the tibia (shin bone), the kneecap (patella), or femur (thighbone) where they connect with the knee.
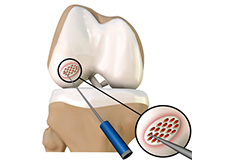
Cartilage Microfracture
Cartilage microfracture is a surgical procedure performed to replace the worn-out articular cartilage with new cartilage.
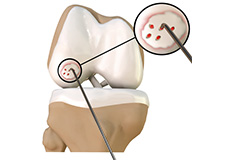
Chondroplasty
Chondroplasty is a surgical procedure to repair and reshape damaged cartilage in a joint. The procedure involves smoothing degenerative cartilage and trimming any unstable flaps of cartilage.

Compartment Decompression
Compartment decompression, also called ‘decompressive fasciotomy’, is a surgical procedure to treat a painful knee condition known as “compartment syndrome”.
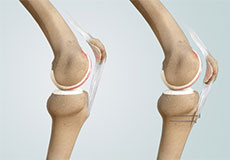
Distal Realignment Procedures
Distal realignment procedures, also known as tibial tubercle transfer (TTT) procedures, are performed to reposition the kneecap after subluxation or dislocation by realigning the tendon under the kneecap to the underlying tibial tubercle.
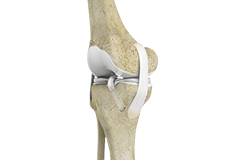
Failed Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
Technical: This is the most common cause of failure and may involve incorrect drilling of a tunnel through the tibial or femoral bone for the attachment of the graft. This may cause increased stress on the graft or rubbing (impingement) of the graft on the surrounding edges of the bone.

Failed Meniscus Repair
Meniscal repair may be performed either by open surgery under direct vision or minimally invasively using an arthroscope, which is a thin tube fitted with a camera that can be inserted into the knee through a very small incision to locate and repair the damaged meniscus.

Hamstring Allograft
An allograft is an organ or tissue such as bone, cartilage, tendon or skin, taken from one person (donor) and surgically placed in another person to repair damaged tissue.
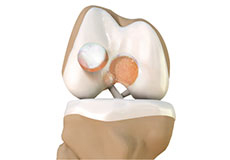
Knee Cartilage Restoration
Knee cartilage restoration is a surgical technique to repair damaged articular cartilage in the knee joint by stimulating new growth of cartilage or by transplanting cartilage into areas with defects in order to relieve pain and restore normal function to the knee.

Lateral Lengthening
Lateral lengthening, also known as lateral retinacular lengthening or release, is a surgical procedure to release a tightened lateral retinaculum on the outer aspect of the knee. This procedure is mostly performed to treat knee pain or patellofemoral instability related to chronic pulling of the patella (kneecap) to the outer aspect of the knee, and the inability of the patella to rest properly in the center of the femoral groove as the knee bends and straightens.

Meniscal Transplantation
Meniscal transplantation is a surgical procedure to replace the damaged meniscus of the knee with healthy cartilage. The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage ring that acts as a cushion between the shinbone and the thighbone. Each of your knees has two menisci - one on the inside (medial aspect) and the other on the outside (lateral aspect) of your knee.
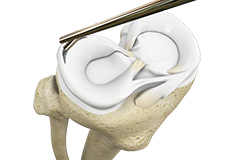
Meniscectomy
Meniscectomy is a surgical procedure indicated in individuals with torn meniscus where the conservative treatments are a failure to relieve the pain and other symptoms. Meniscectomy is recommended based on the ability of meniscus to heal, patient’s age, health status, and activity level.
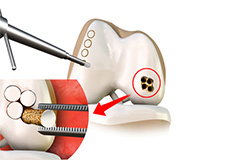
Mosaicplasty
Weight-bearing joints, such as the knee, may develop defects in the articular cartilage (spongy tissue that lines and cushions joints during movement) due to stress, trauma or degenerative disease. This can lead to pain, swelling or locking at the joint.

Partial Arthroscopic Meniscectomy
Partial arthroscopic meniscectomy is a procedure to remove the damaged part of a meniscus in the knee joint with the help an arthroscope. The meniscus is a C-shaped disc of cartilage between your thighbone and shinbone.

Partial Meniscectomy
Partial meniscectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the torn portion of the meniscus from the knee joint. Meniscal tears can occur at any age, but are more common in athletes playing contact sports. These tears are usually caused by twisting motion or over-flexing of the knee joint.

Patellofemoral Realignment
Patellofemoral realignment is a surgical procedure performed to treat symptomatic patellofemoral instability that does not respond to nonsurgical treatment measures.
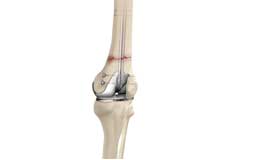
Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Fixation
Periprosthetic knee fracture fixation is a procedure performed to stabilize a fracture that occurs in the bone present around a knee prosthesis. The fracture may involve the lower part of the thighbone (femur), the kneecap (patella) or the upper part of the shinbone (tibia).

Robotic Assisted Partial Knee Surgery
Robotic-assisted partial knee surgery is an innovative alternative to the conventional surgical procedure to treat degenerative knee diseases such as osteoarthritis. It is performed using robotic-arm technology that allows your surgeon to precisely perform the surgery through small incisions.

Signature Knees
Signature knee is a unique knee replacement procedure that is tailored to suit your individual anatomy. The technique utilizes magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology to create 3D images of your knee joint, which enables your doctor to efficiently plan your knee replacement surgery.
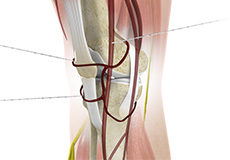
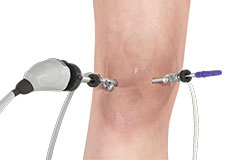
Genicular Nerve Block
A genicular nerve block is a minimally invasive procedure where anesthetic medication is injected into one or more of the genicular nerves to control pain. Three main genicular nerves supply the knee joint: the superior lateral genicular nerve, the superior medial genicular nerve, and the inferior medial genicular nerve.

Ultrasound-Guided Genicular Nerve Block
The genicular nerves are nerves surrounding your knee joint that are responsible for the transmission of pain impulses. Knee disorders causing excessive pain can be treated by blocking the genicular nerves from transmitting nerve impulses. The procedure may be performed under the guidance of ultrasound imaging.
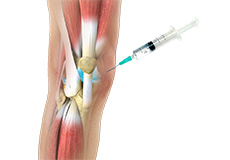
Viscosupplementation
Viscosupplementation refers to the injection of a hyaluronan preparation into the joint. Hyaluronan is a natural substance present in the joint fluid that assists in lubrication. It allows the smooth movement of the cartilage-covered articulating surfaces of the joint.

N-stride Injection
N-stride injection is used to treat knee osteoarthritis. It is prepared from blood extracted from your body and is rich in anabolic growth factors, special proteins involved in the body’s healing process and anti-in?ammatory proteins responsible for suppressing inflammation in your knee joints.

Intraarticluar Knee Injection
Knee pain and stiffness can be disabling and difficult to treat. It can limit an individual’s lifestyle and negatively impact body image and emotional well-being.

Pharmacological Interventions for Knee Injuries
Pharmacological interventions include medicinal preparations such as pain-relieving capsules or injections. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: These are known as NSAIDs and are found to be effective in reducing pain and inflammation in the knee.
What is New in Knee Replacement
If you are considering knee replacement surgery, there are new developments under study which can help enhance the quality of life. Use of cementless parts that allow new bone to grow into a porous prosthesis and hold the parts in place, creating a biologic fixation

Rapid Recovery Knee Replacement
Coming soon
Others

Am I a Candidate for Knee Surgery?
Arthritis of the knee can cause pain and stiffness, making regular activities such as walking and bending difficult. As arthritis progresses, conservative treatments tend to lose their efficacy and more definitive treatment should be considered.

Knee Implants
Knee implants are artificial devices that form the essential parts of the knee during a knee replacement surgery. The knee implants vary by size, shape, and material. Implants are made of biocompatible materials that are accepted by the body without producing any rejection response.

Knee Implants for Women
Knee replacement surgery may be associated with pain and limited motion if an implant does not suit your particular anatomy. Implants specific to women’s knee are provided by some companies like Zimmer and Biomet.
Physical Examination of the Knee
A complete physical examination of the knee is performed when you present to your doctor with a knee complaint. Both of your knees are examined and the results of the injured knee are compared to those of the healthy knee.
Non-Surgical Knee Treatments
The knee is a complex joint which consists of bone, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons that make joint movements easy and at the same time it is more susceptible to various kinds of injuries. Knee problems may arise if any of these structures get injured by overuse or suddenly during sports activities.

Nonoperative Treatments for ACL Injuries
The ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) is one of the four major ligaments located within the knee joint. It connects the femur (thighbone) to the tibia (shinbone). It plays a key role in holding the two bones within the knee and keeping the joint stable while your knee moves back and forth.

